HOW TO IMPORT CSTATISTIC.H PACKAGES IN OMNET++
The cStatistic Header serves as a crucial element for the collection and management of statistical data during simulations. It establishes a structure for documenting and analyzing various metrics, including throughput, delay, and packet loss, which are vital for assessing the performance and behavior of network models. cStatistic is utilized to monitor quantitative data throughout the simulation, facilitating a variety of statistical functions such as calculating averages, variances, and percentiles. It is capable of processing different data types, including scalar values and histograms, and offers methods for updating, querying, and resetting statistics. This class is frequently employed alongside other OMNeT++ components to gather data from simulation modules and channels. By integrating cStatistic, developers can derive insights from their simulation outcomes, visualize performance metrics, and make informed decisions regarding network design or behavior..
Follow our guidelines to run CSTATISTIC.H_ omnet++ program
PRE-REQUISITES:
- Fresh installation of Windows 10:
Screenshot:

2.OMNET++ Installation:
Screenshot
HEADER FILE VERIFICATION:
- Locate to the Examples:
Screenshot:
2.OMNeT++ Building Process:
Next, we need to build the Aloha folder to make Aloha Example to work in the OMNET++ 6.0.2 IDE. Right Click the Aloha folder and Click the Build Project Option to build the Aloha Folder.
Screenshot:
Here, we shown the Aloha Building Process.
Screenshot:
Screenshot:
Screenshot:
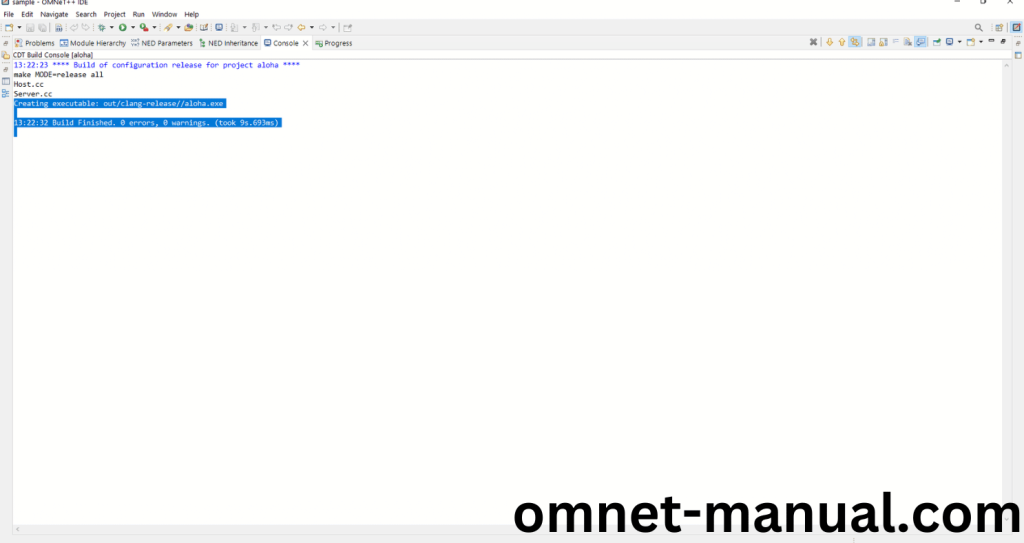
Here We successfully built and imported the Aloha Example in the OMNET++ IDE.
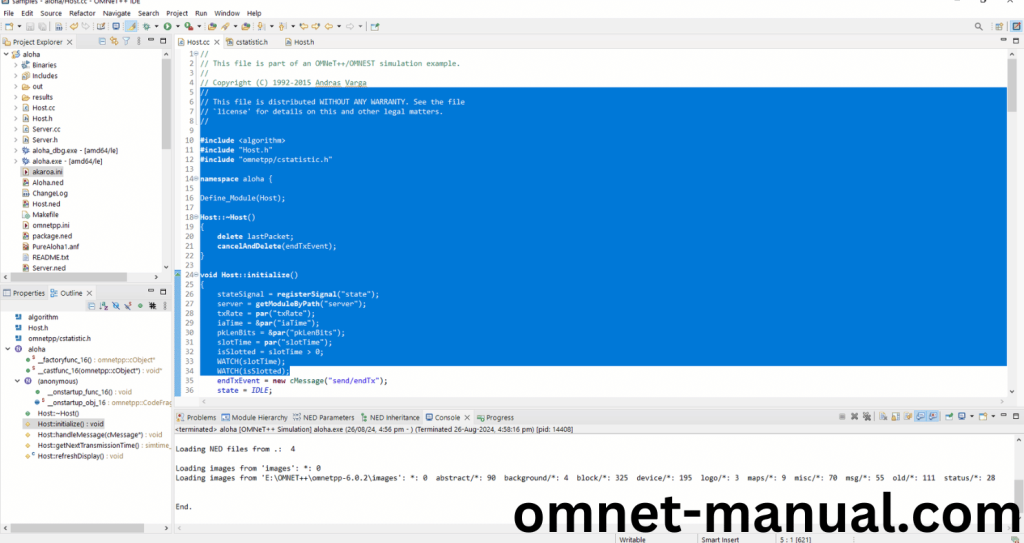
3.Importing cStatistic.h:
Here we imported the cStatistic.h header file in this example program by clicking the Host.cc, you can see the header imported. So here we need to add code for cStatistic header in the existing code of Aloha Example.
Code for Host.h:
private:
cOutVector pkCounterVector; // Vector for storing the number of packets transmitted
cOutVector txDurationVector; // Vector for storing the duration of each transmission
Code for Host.cc:
#include <algorithm>
#include “Host.h”
#include “omnetpp/cstatistic.h”
namespace aloha {
Define_Module(Host);
Host::~Host()
{
delete lastPacket;
cancelAndDelete(endTxEvent);
}
void Host::initialize()
{
stateSignal = registerSignal(“state”);
server = getModuleByPath(“server”);
txRate = par(“txRate”);
iaTime = &par(“iaTime”);
pkLenBits = &par(“pkLenBits”);
slotTime = par(“slotTime”);
isSlotted = slotTime > 0;
WATCH(slotTime);
WATCH(isSlotted);
endTxEvent = new cMessage(“send/endTx”);
state = IDLE;
emit(stateSignal, state);
pkCounter = 0;
WATCH((int&)state);
WATCH(pkCounter);
x = par(“x”).doubleValue();
y = par(“y”).doubleValue();
double serverX = server->par(“x”).doubleValue();
double serverY = server->par(“y”).doubleValue();
idleAnimationSpeed = par(“idleAnimationSpeed”);
transmissionEdgeAnimationSpeed = par(“transmissionEdgeAnimationSpeed”);
midtransmissionAnimationSpeed = par(“midTransmissionAnimationSpeed”);
double dist = std::sqrt((x-serverX) * (x-serverX) + (y-serverY) * (y-serverY));
radioDelay = dist / propagationSpeed;
getDisplayString().setTagArg(“p”, 0, x);
getDisplayString().setTagArg(“p”, 1, y);
scheduleAt(getNextTransmissionTime(), endTxEvent);
pkCounterVector.setName(“packetCounter”);
txDurationVector.setName(“transmissionDuration”);
}
void Host::handleMessage(cMessage *msg)
{
ASSERT(msg == endTxEvent);
getParentModule()->getCanvas()->setAnimationSpeed(transmissionEdgeAnimationSpeed, this);
if (state == IDLE) {
char pkname[40];
sprintf(pkname, “pk-%d-#%d”, getId(), pkCounter++);
EV << “generating packet ” << pkname << endl;
state = TRANSMIT;
emit(stateSignal, state);
cPacket *pk = new cPacket(pkname);
pk->setBitLength(pkLenBits->intValue());
simtime_t duration = pk->getBitLength() / txRate;
sendDirect(pk, radioDelay, duration, server->gate(“in”));
scheduleAt(simTime()+duration, endTxEvent);
pkCounterVector.record(pkCounter);
txDurationVector.record(duration.dbl());
if (transmissionRing != nullptr) {
delete lastPacket;
lastPacket = pk->dup();
}
}
else if (state == TRANSMIT) {
state = IDLE;
emit(stateSignal, state);
scheduleAt(getNextTransmissionTime(), endTxEvent);
}
else {
throw cRuntimeError(“invalid state”);
}
}
simtime_t Host::getNextTransmissionTime()
{
simtime_t t = simTime() + iaTime->doubleValue();
if (!isSlotted)
return t;
else
return slotTime * ceil(t/slotTime);
}
void Host::refreshDisplay() const
{
cCanvas *canvas = getParentModule()->getCanvas();
const int numCircles = 20;
const double circleLineWidth = 10;
if (!transmissionRing) {
auto color = cFigure::GOOD_DARK_COLORS[getId() % cFigure::NUM_GOOD_DARK_COLORS];
transmissionRing = new cRingFigure((“Host” + std::to_string(getIndex()) + “Ring”).c_str());
transmissionRing->setOutlined(false);
transmissionRing->setFillColor(color);
transmissionRing->setFillOpacity(0.25);
transmissionRing->setFilled(true);
transmissionRing->setVisible(false);
transmissionRing->setZIndex(-1);
canvas->addFigure(transmissionRing);
for (int i = 0; i < numCircles; ++i) {
auto circle = new cOvalFigure((“Host” + std::to_string(getIndex()) + “Circle” + std::to_string(i)).c_str());
circle->setFilled(false);
circle->setLineColor(color);
circle->setLineOpacity(0.75);
circle->setLineWidth(circleLineWidth);
circle->setZoomLineWidth(true);
circle->setVisible(false);
circle->setZIndex(-0.5);
transmissionCircles.push_back(circle);
canvas->addFigure(circle);
}
}
if (lastPacket) {
if (transmissionRing->getAssociatedObject() != lastPacket) {
transmissionRing->setAssociatedObject(lastPacket);
for (auto c : transmissionCircles)
c->setAssociatedObject(lastPacket);
}
simtime_t now = simTime();
simtime_t frontTravelTime = now – lastPacket->getSendingTime();
simtime_t backTravelTime = now – (lastPacket->getSendingTime() + lastPacket->getDuration());
double frontRadius = std::min(ringMaxRadius, frontTravelTime.dbl() * propagationSpeed);
double backRadius = backTravelTime.dbl() * propagationSpeed;
double circleRadiusIncrement = circlesMaxRadius / numCircles;
double opacity = 1.0;
if (backRadius > ringMaxRadius) {
transmissionRing->setVisible(false);
transmissionRing->setAssociatedObject(nullptr);
}
else {
transmissionRing->setVisible(true);
transmissionRing->setBounds(cFigure::Rectangle(x – frontRadius, y – frontRadius, 2*frontRadius, 2*frontRadius));
transmissionRing->setInnerRadius(std::max(0.0, std::min(ringMaxRadius, backRadius)));
if (backRadius > 0)
opacity = std::max(0.0, 1.0 – backRadius / circlesMaxRadius);
}
transmissionRing->setLineOpacity(opacity);
transmissionRing->setFillOpacity(opacity/5);
double radius0 = std::fmod(frontTravelTime.dbl() * propagationSpeed, circleRadiusIncrement);
for (int i = 0; i < (int)transmissionCircles.size(); ++i) {
double circleRadius = std::min(ringMaxRadius, radius0 + i * circleRadiusIncrement);
if (circleRadius < frontRadius – circleRadiusIncrement/2 && circleRadius > backRadius + circleLineWidth/2) {
transmissionCircles[i]->setVisible(true);
transmissionCircles[i]->setBounds(cFigure::Rectangle(x – circleRadius, y – circleRadius, 2*circleRadius, 2*circleRadius));
transmissionCircles[i]->setLineOpacity(std::max(0.0, 0.2 – 0.2 * (circleRadius / circlesMaxRadius)));
}
else
transmissionCircles[i]->setVisible(false);
}
double animSpeed = idleAnimationSpeed;
if ((frontRadius >= 0 && frontRadius < circlesMaxRadius) || (backRadius >= 0 && backRadius < circlesMaxRadius))
animSpeed = transmissionEdgeAnimationSpeed;
if (frontRadius > circlesMaxRadius && backRadius < 0)
animSpeed = midtransmissionAnimationSpeed;
canvas->setAnimationSpeed(animSpeed, this);
}
else {
if (transmissionRing->getAssociatedObject() != nullptr) {
transmissionRing->setVisible(false);
transmissionRing->setAssociatedObject(nullptr);
for (auto c : transmissionCircles) {
c->setVisible(false);
c->setAssociatedObject(nullptr);
}
canvas->setAnimationSpeed(idleAnimationSpeed, this);
}
}
getDisplayString().setTagArg(“t”, 2, “#808000”);
if (state == IDLE) {
getDisplayString().setTagArg(“i”, 1, “”);
getDisplayString().setTagArg(“t”, 0, “”);
}
else if (state == TRANSMIT) {
getDisplayString().setTagArg(“i”, 1, “yellow”);
getDisplayString().setTagArg(“t”, 0, “TRANSMIT”);
}
}
}; //namespace
Press Control key and click the cStatistic.h to open the header file.
Screenshot:
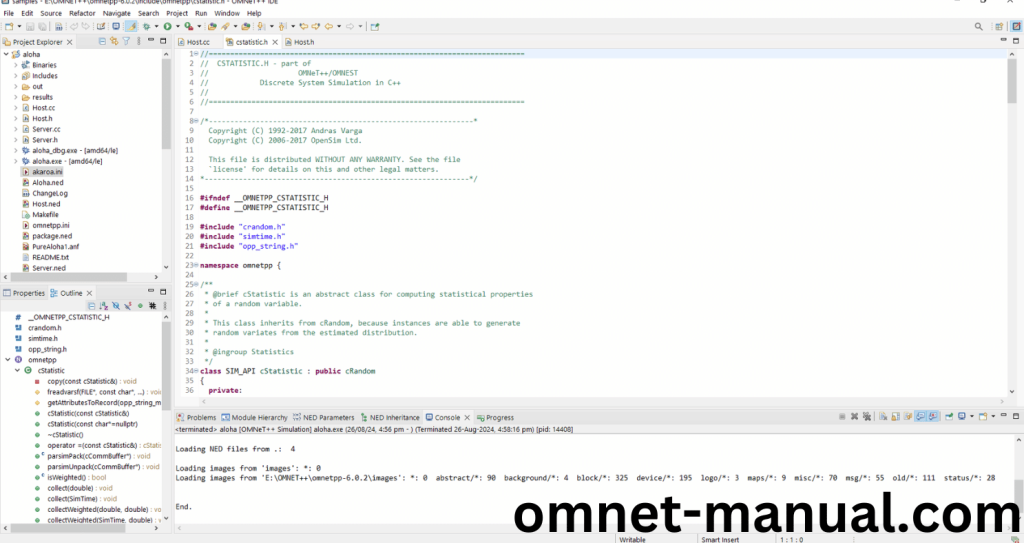
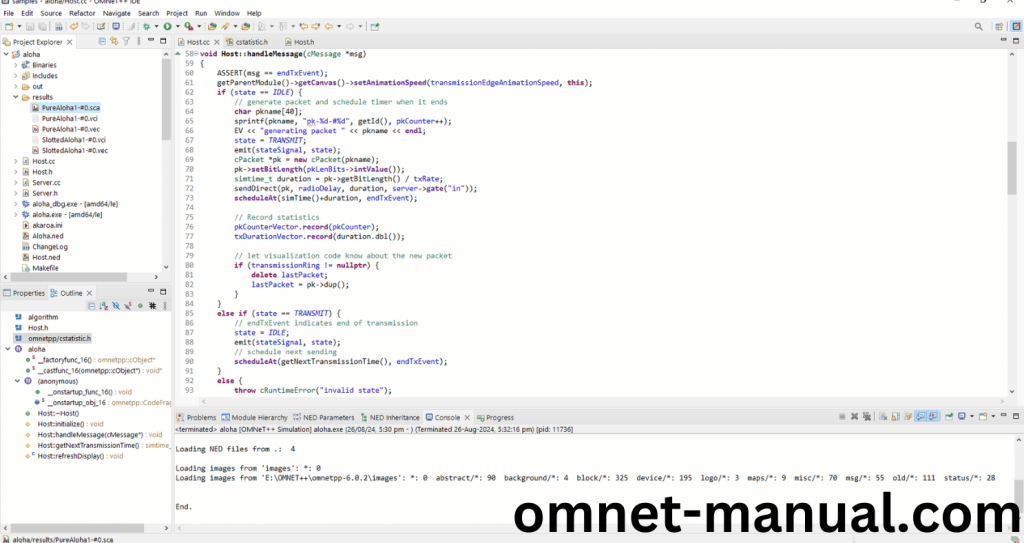
Here we will show the cStatistic.h header file to show the highlighted line imported from the cStatistic.h in the example code in function handleMessage().
Screenshot:
4.Executing the Example Program Using cStatistic header file:
Then we need to run the Example program Using cStatistic header file to view output of the program. Firstly, we need to locate to the “/Aloha/” to find the example program in the Aloha Folder.
Screenshot:
Next click the “omnetpp.ini” file and Configuration of the Aloha Program.
Screenshot:
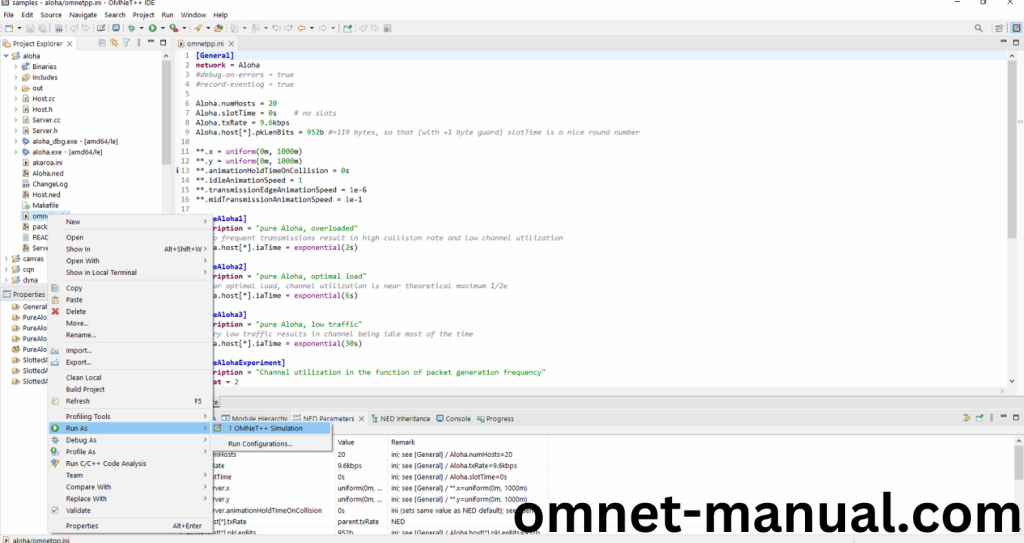
Next, Right Click the omnetpp.ini file, click the Run As and then Click the OMNeT++ Simulation.
Screenshot:
If you got any prompt, then Click the OK button to build and Simulate the Example program.
Screenshot:
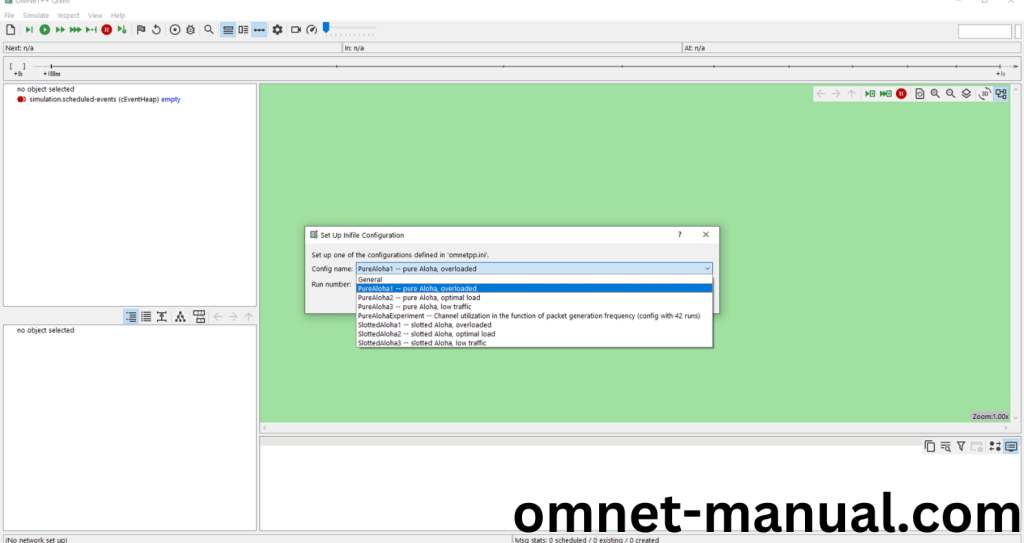
Click the Any Configuration in the Omnet++ Ide to select the Configuration for the Example Program Simulation.
Screenshot:
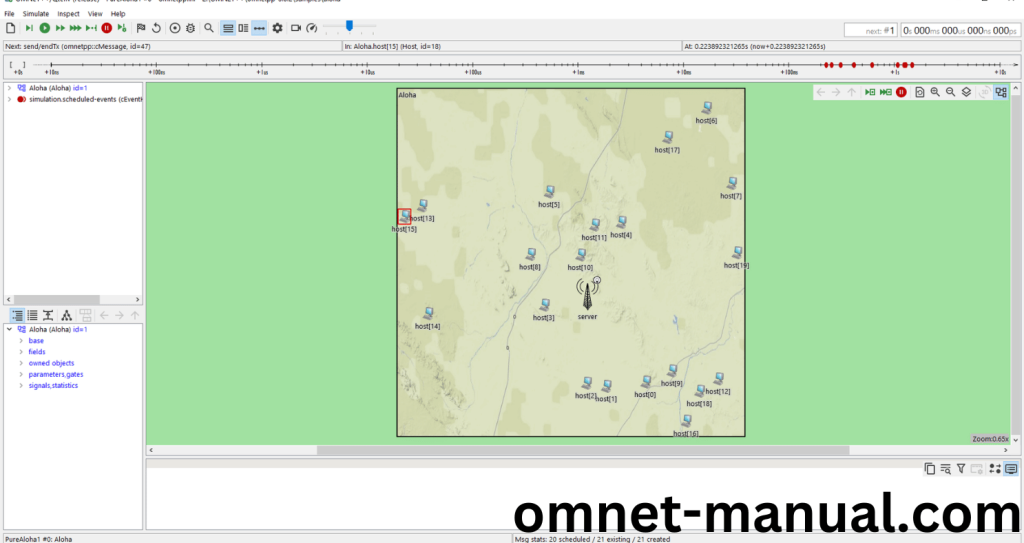
Click the Run Button in the Omnet++ Ide to simulate the Example Program.
Screenshot:
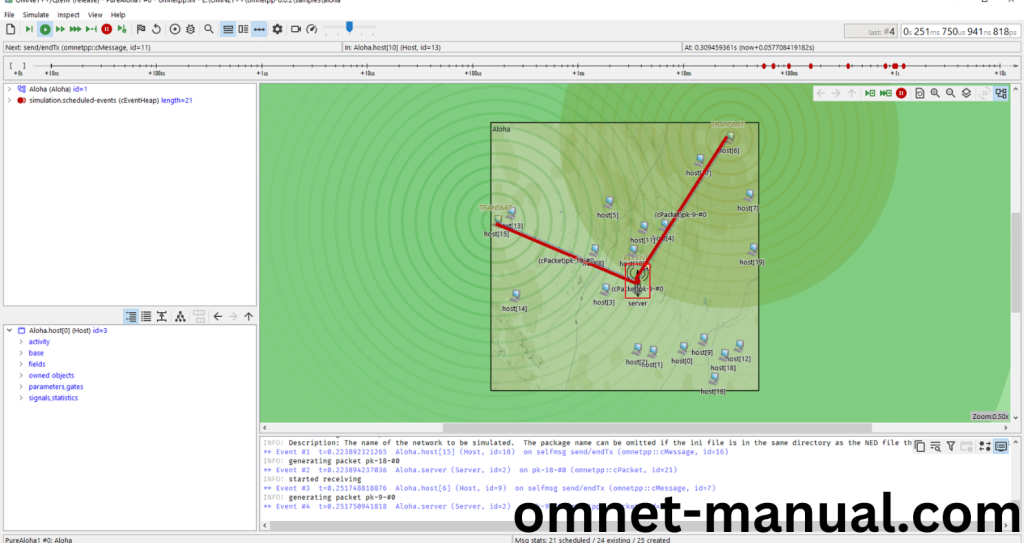
Screenshot:
Screenshot:
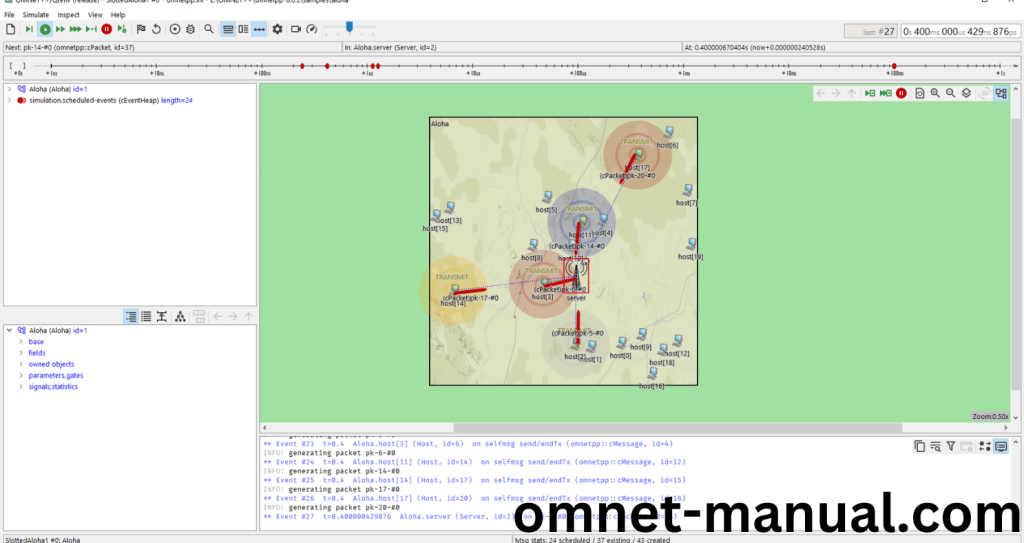
Next Locate to the Result folder and You can see the PureAloha1-#0.sca file.Click it
Screenshot:
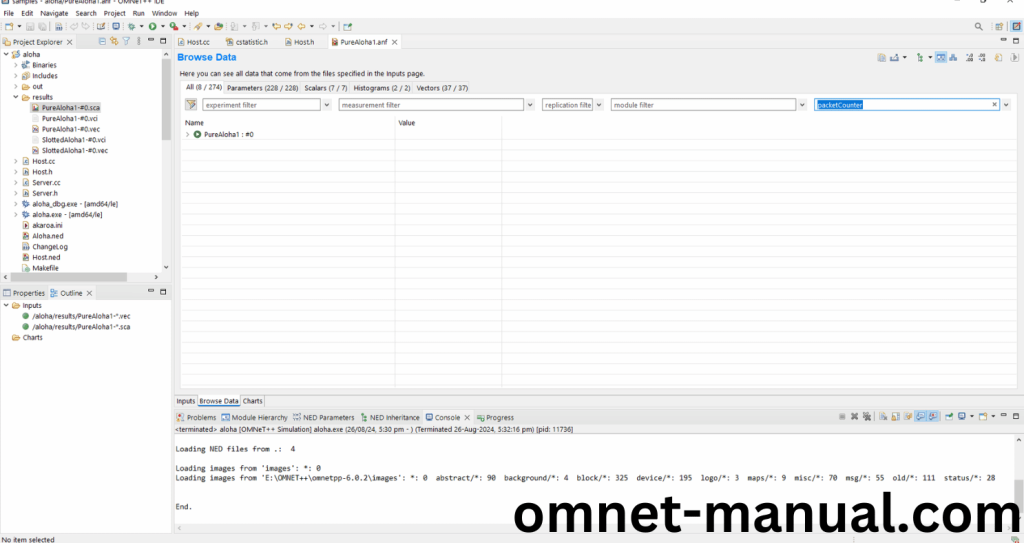
Next click Browse Data and search for PacketCounter or TransmissionDuration that we have modified in this Code based on the cStatistic.h Header file, then click PureAloha1 and finally You can view the Statistic Graph.
Screenshot:
Screenshot:
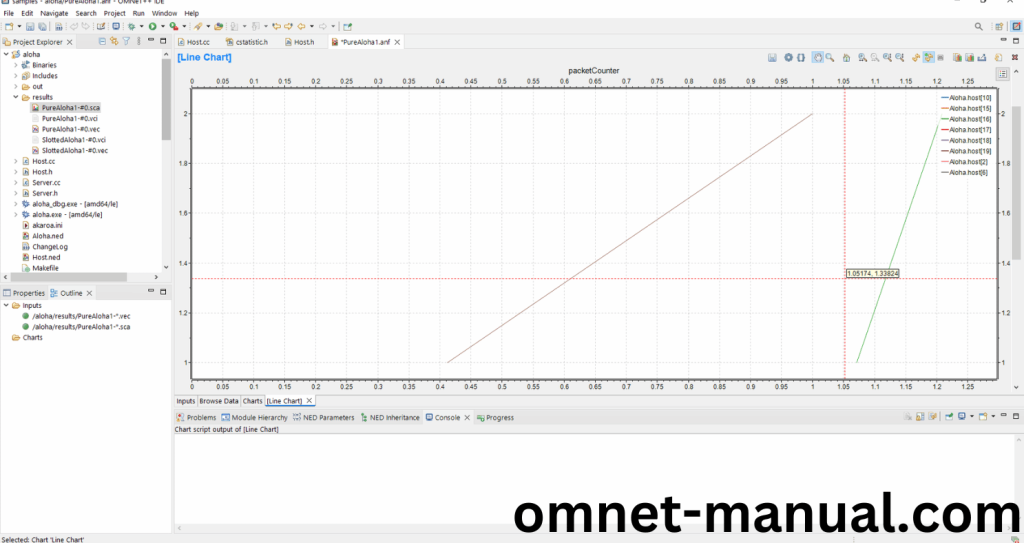
Simulation Completed Successfully by the Aloha Example Using cStatistic header.
We offer detailed guidance and installation assistance for using the CSTATISTIC.H packages within the OMNeT++ tool. Furthermore, we present a variety of creative project ideas, each with clear explanations. Keep in touch with us to achieve the best results.
