HOW TO IMPORT CRESULTRECORDER.H PACKAGES in OMNET++
CRESULTRECORDER.H_ installation in omnet++ tool are shared we have an exciting and exclusive article that is just popped out for you to notify the steps that are required. The cResultRecorder header is all about keeping track of simulation results like scalars, vectors, and histograms while a simulation runs. The cResultRecorder class makes it super easy to gather and save all sorts of performance metrics and data points that come from simulation models. With Data Recording, you can log different kinds of results, including scalar values (like average delay), time-series data (like how many packets arrive over time), and statistical summaries (like histograms). It can kick in during certain events in the simulation, like when a message arrives or a task wraps up, so it captures the important data right when it matters.
PRE-REQUISITES:
- Fresh installation of Windows 10:
Screenshot:

2.OMNET++ Installation:
Screenshot:
HEADER FILE VERIFICATION:
- Locate to the Examples:
Screenshot:
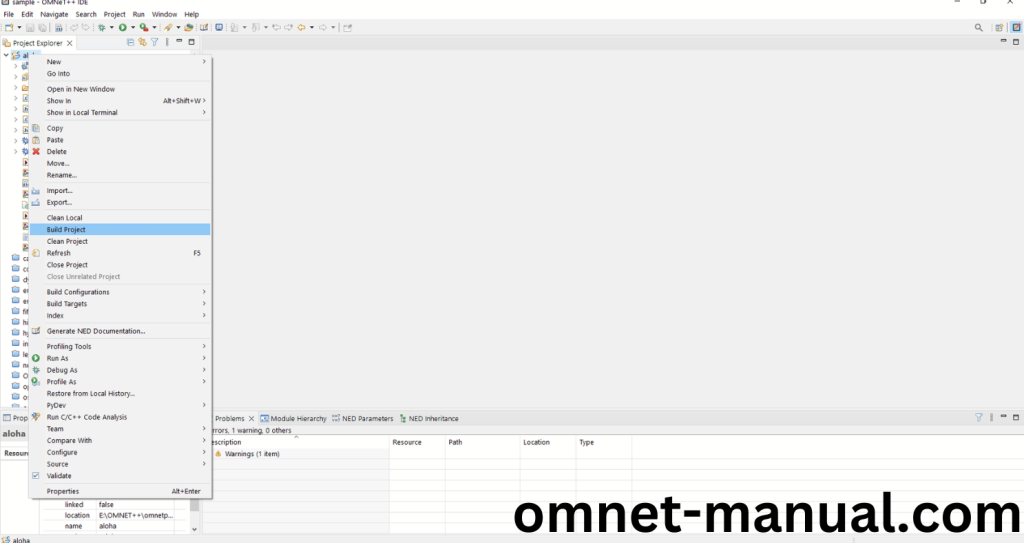
2.OMNeT++ Building Process:
Next, we need to build the Aloha folder to make Aloha Example to work in the OMNET++ 6.0.2 IDE. Right Click the Aloha folder and Click the Build Project Option to build the Aloha Folder.
Screenshot:
Here, we shown the Aloha Building Process.
Screenshot:
Screenshot:
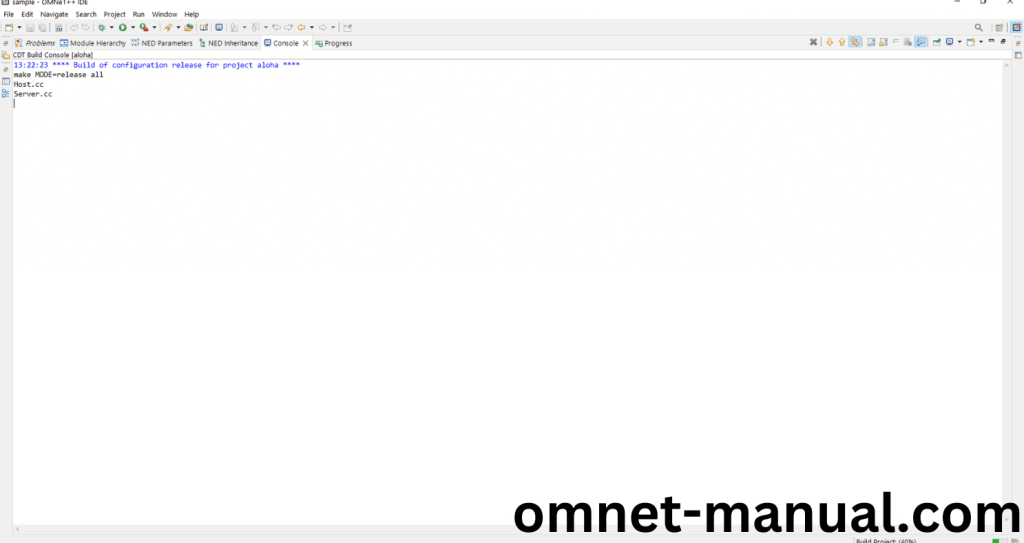
Screenshot:
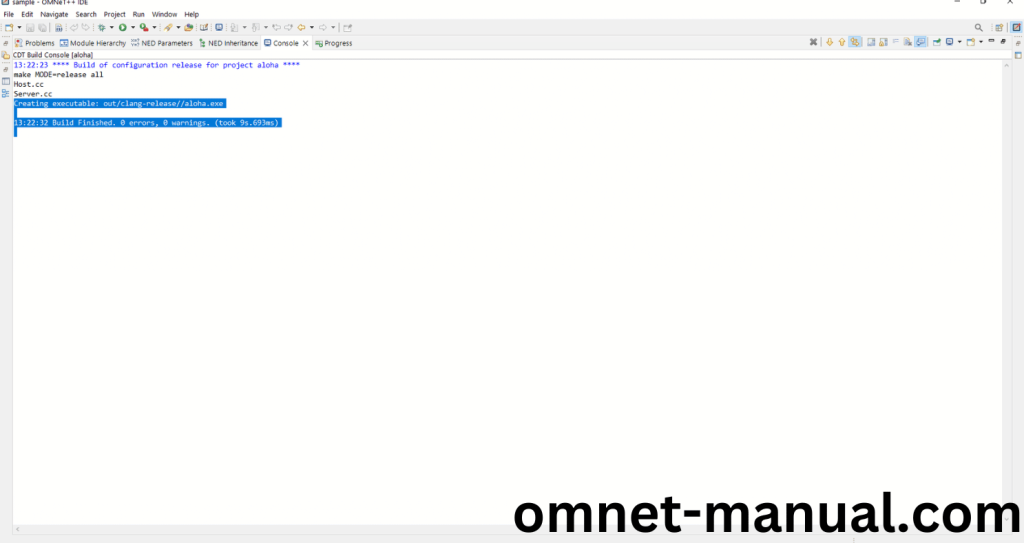
Here We successfully built and imported the Aloha Example in the OMNET++ IDE.
3.Importing cResultRecorder.h:
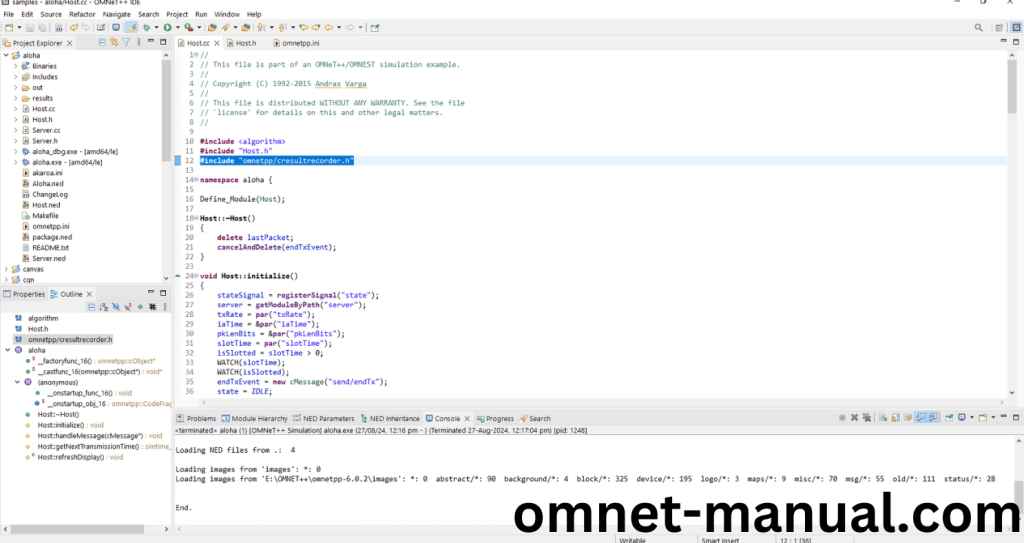
Here we imported the cResultRecorder.h header file in this example program by clicking the Host.cc, you can see the header imported.
Screenshot:
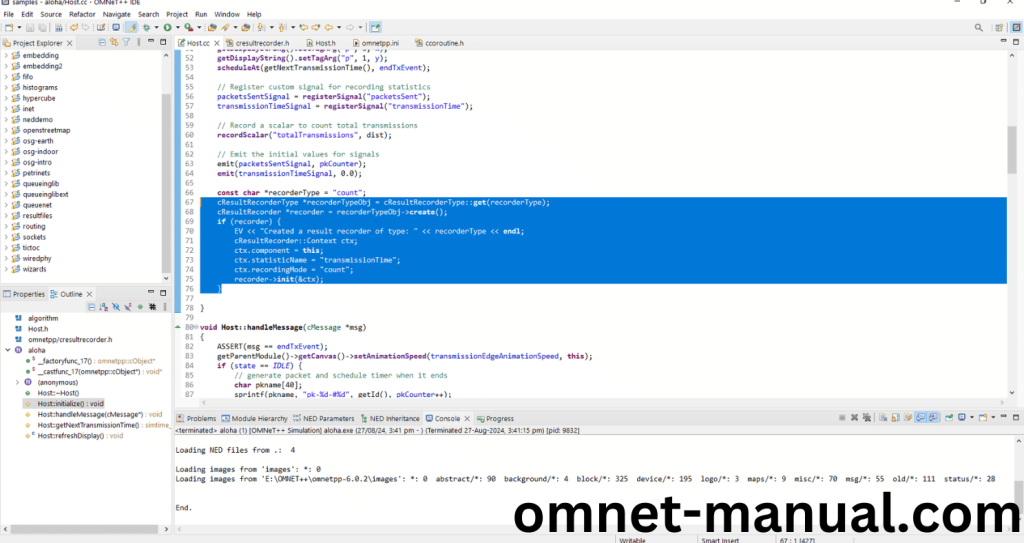
So here we need to copy this code and paste in the existing codes of Aloha Example for cResultRecorder header.
Code for Host.cc:
#include <algorithm>
#include “Host.h”
#include “omnetpp/cresultrecorder.h”
namespace aloha {
Define_Module(Host);
Host::~Host()
{
delete lastPacket;
cancelAndDelete(endTxEvent);
}
void Host::initialize()
{
stateSignal = registerSignal(“state”);
server = getModuleByPath(“server”);
txRate = par(“txRate”);
iaTime = &par(“iaTime”);
pkLenBits = &par(“pkLenBits”);
slotTime = par(“slotTime”);
isSlotted = slotTime > 0;
WATCH(slotTime);
WATCH(isSlotted);
endTxEvent = new cMessage(“send/endTx”);
state = IDLE;
emit(stateSignal, state);
pkCounter = 0;
WATCH((int&)state);
WATCH(pkCounter);
x = par(“x”).doubleValue();
y = par(“y”).doubleValue();
double serverX = server->par(“x”).doubleValue();
double serverY = server->par(“y”).doubleValue();
idleAnimationSpeed = par(“idleAnimationSpeed”);
transmissionEdgeAnimationSpeed = par(“transmissionEdgeAnimationSpeed”);
midtransmissionAnimationSpeed = par(“midTransmissionAnimationSpeed”);
double dist = std::sqrt((x-serverX) * (x-serverX) + (y-serverY) * (y-serverY));
radioDelay = dist / propagationSpeed;
getDisplayString().setTagArg(“p”, 0, x);
getDisplayString().setTagArg(“p”, 1, y);
scheduleAt(getNextTransmissionTime(), endTxEvent);
// Register custom signal for recording statistics
packetsSentSignal = registerSignal(“packetsSent”);
transmissionTimeSignal = registerSignal(“transmissionTime”);
// Record a scalar to count total transmissions
recordScalar(“totalTransmissions”, dist);
// Emit the initial values for signals
emit(packetsSentSignal, pkCounter);
emit(transmissionTimeSignal, 0.0);
const char *recorderType = “count”;
cResultRecorderType *recorderTypeObj = cResultRecorderType::get(recorderType);
cResultRecorder *recorder = recorderTypeObj->create();
if (recorder) {
EV << “Created a result recorder of type: ” << recorderType << endl;
cResultRecorder::Context ctx;
ctx.component = this;
ctx.statisticName = “transmissionTime”;
ctx.recordingMode = “count”;
recorder->init(&ctx);
}
}
void Host::handleMessage(cMessage *msg)
{
ASSERT(msg == endTxEvent);
getParentModule()->getCanvas()->setAnimationSpeed(transmissionEdgeAnimationSpeed, this);
if (state == IDLE) {
char pkname[40];
sprintf(pkname, “pk-%d-#%d”, getId(), pkCounter++);
EV << “generating packet ” << pkname << endl;
state = TRANSMIT;
emit(stateSignal, state);
cPacket *pk = new cPacket(pkname);
pk->setBitLength(pkLenBits->intValue());
// Emit signal for number of packets sent
emit(packetsSentSignal, pkCounter);
simtime_t duration = pk->getBitLength() / txRate;
sendDirect(pk, radioDelay, duration, server->gate(“in”));
// Emit signal for transmission time
emit(transmissionTimeSignal, duration.dbl());
scheduleAt(simTime()+duration, endTxEvent);
if (transmissionRing != nullptr) {
delete lastPacket;
lastPacket = pk->dup();
}
}
else if (state == TRANSMIT) {
state = IDLE;
emit(stateSignal, state);
scheduleAt(getNextTransmissionTime(), endTxEvent);
}
else {
throw cRuntimeError(“invalid state”);
}
}
simtime_t Host::getNextTransmissionTime()
{
simtime_t t = simTime() + iaTime->doubleValue();
if (!isSlotted)
return t;
else
return slotTime * ceil(t/slotTime);
}
void Host::refreshDisplay() const
{
cCanvas *canvas = getParentModule()->getCanvas();
const int numCircles = 20;
const double circleLineWidth = 10;
if (!transmissionRing) {
auto color = cFigure::GOOD_DARK_COLORS[getId() % cFigure::NUM_GOOD_DARK_COLORS];
transmissionRing = new cRingFigure((“Host” + std::to_string(getIndex()) + “Ring”).c_str());
transmissionRing->setOutlined(false);
transmissionRing->setFillColor(color);
transmissionRing->setFillOpacity(0.25);
transmissionRing->setFilled(true);
transmissionRing->setVisible(false);
transmissionRing->setZIndex(-1);
canvas->addFigure(transmissionRing);
for (int i = 0; i < numCircles; ++i) {
auto circle = new cOvalFigure((“Host” + std::to_string(getIndex()) + “Circle” + std::to_string(i)).c_str());
circle->setFilled(false);
circle->setLineColor(color);
circle->setLineOpacity(0.75);
circle->setLineWidth(circleLineWidth);
circle->setZoomLineWidth(true);
circle->setVisible(false);
circle->setZIndex(-0.5);
transmissionCircles.push_back(circle);
canvas->addFigure(circle);
}
}
if (lastPacket) {
if (transmissionRing->getAssociatedObject() != lastPacket) {
transmissionRing->setAssociatedObject(lastPacket);
for (auto c : transmissionCircles)
c->setAssociatedObject(lastPacket);
}
simtime_t now = simTime();
simtime_t frontTravelTime = now – lastPacket->getSendingTime();
simtime_t backTravelTime = now – (lastPacket->getSendingTime() + lastPacket->getDuration());
double frontRadius = std::min(ringMaxRadius, frontTravelTime.dbl() * propagationSpeed);
double backRadius = backTravelTime.dbl() * propagationSpeed;
double circleRadiusIncrement = circlesMaxRadius / numCircles;
double opacity = 1.0;
if (backRadius > ringMaxRadius) {
transmissionRing->setVisible(false);
transmissionRing->setAssociatedObject(nullptr);
}
else {
transmissionRing->setVisible(true);
transmissionRing->setBounds(cFigure::Rectangle(x – frontRadius, y – frontRadius, 2*frontRadius, 2*frontRadius));
transmissionRing->setInnerRadius(std::max(0.0, std::min(ringMaxRadius, backRadius)));
if (backRadius > 0)
opacity = std::max(0.0, 1.0 – backRadius / circlesMaxRadius);
}
transmissionRing->setLineOpacity(opacity);
transmissionRing->setFillOpacity(opacity/5);
double radius0 = std::fmod(frontTravelTime.dbl() * propagationSpeed, circleRadiusIncrement);
for (int i = 0; i < (int)transmissionCircles.size(); ++i) {
double circleRadius = std::min(ringMaxRadius, radius0 + i * circleRadiusIncrement);
if (circleRadius < frontRadius – circleRadiusIncrement/2 && circleRadius > backRadius + circleLineWidth/2) {
transmissionCircles[i]->setVisible(true);
transmissionCircles[i]->setBounds(cFigure::Rectangle(x – circleRadius, y – circleRadius, 2*circleRadius, 2*circleRadius));
transmissionCircles[i]->setLineOpacity(std::max(0.0, 0.2 – 0.2 * (circleRadius / circlesMaxRadius)));
}
else
transmissionCircles[i]->setVisible(false);
}
double animSpeed = idleAnimationSpeed;
if ((frontRadius >= 0 && frontRadius < circlesMaxRadius) || (backRadius >= 0 && backRadius < circlesMaxRadius))
animSpeed = transmissionEdgeAnimationSpeed;
if (frontRadius > circlesMaxRadius && backRadius < 0)
animSpeed = midtransmissionAnimationSpeed;
canvas->setAnimationSpeed(animSpeed, this);
}
else {
if (transmissionRing->getAssociatedObject() != nullptr) {
transmissionRing->setVisible(false);
transmissionRing->setAssociatedObject(nullptr);
for (auto c : transmissionCircles) {
c->setVisible(false);
c->setAssociatedObject(nullptr);
}
canvas->setAnimationSpeed(idleAnimationSpeed, this);
}
}
getDisplayString().setTagArg(“t”, 2, “#808000”);
if (state == IDLE) {
getDisplayString().setTagArg(“i”, 1, “”);
getDisplayString().setTagArg(“t”, 0, “”);
}
else if (state == TRANSMIT) {
getDisplayString().setTagArg(“i”, 1, “yellow”);
getDisplayString().setTagArg(“t”, 0, “TRANSMIT”);
}}}; //namespace
Code for Host.h:
simsignal_t packetsSentSignal;
simsignal_t transmissionTimeSignal;
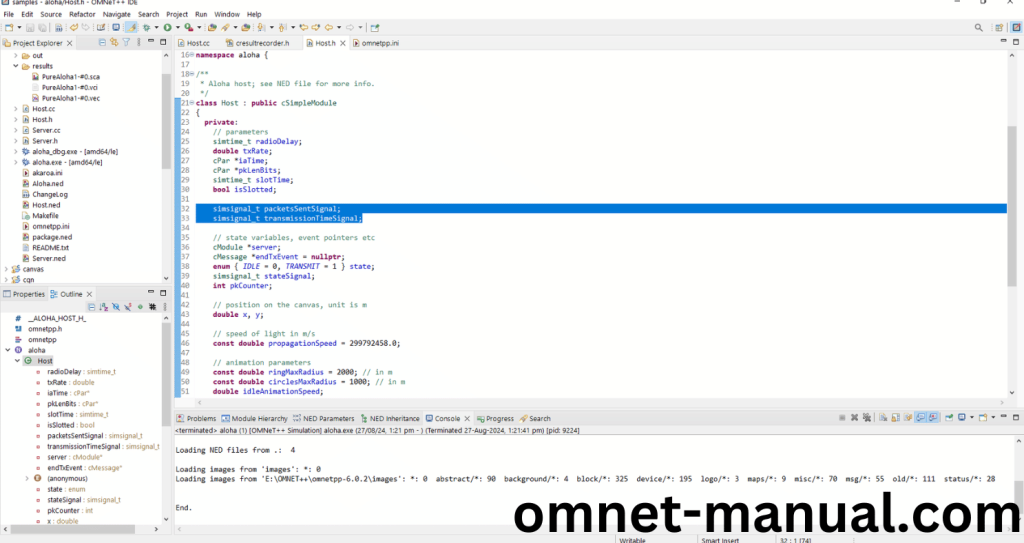
Code for omnetpp.ini:
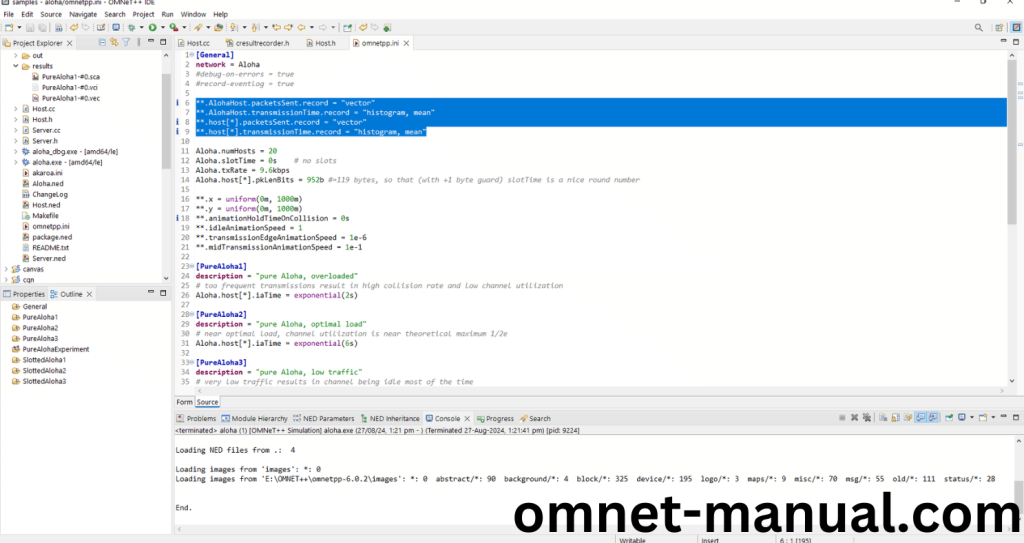
**.AlohaHost.packetsSent.record = “vector”
**.AlohaHost.transmissionTime.record = “histogram, mean”
**.host[*].packetsSent.record = “vector”
**.host[*].transmissionTime.record = “histogram, mean”
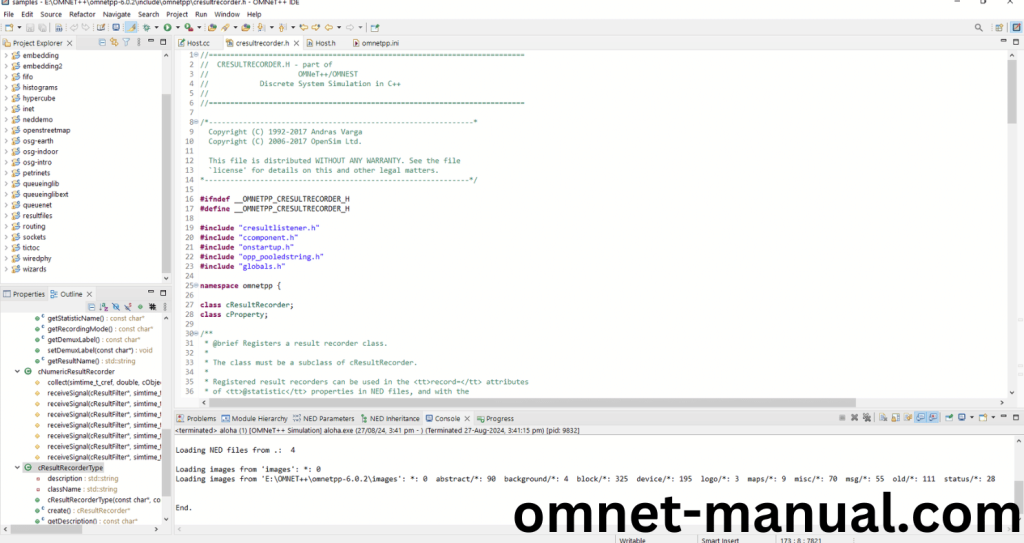
Press Control key and click the cResultRecorder.h to open the header file.
Screenshot:
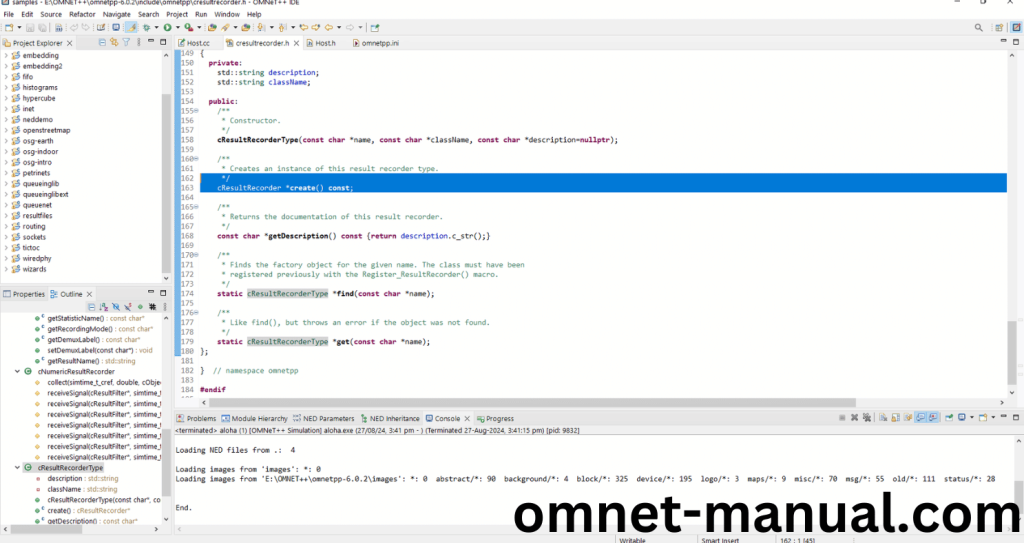
Here we will show the cResultRecorder.h header file to show the highlighted line imported from the cResultRecorder.h in the example code in function handleMessage().
Screenshot:
4.Executing the Example Program Using cResultRecorder header file:
Then we need to run the Example program Using cResultRecorder header file to view output of the program. Firstly, we need to locate to the “/Aloha/” to find the example program in the Aloha Folder.
Screenshot:
Next click the “omnetpp.ini” file and Configuration of the Aloha Program.
Screenshot:
Next, Right Click the omnetpp.ini file, click the Run As and then Click the OMNeT++ Simulation.
Screenshot:

If you got any prompt, then Click the OK button to build and Simulate the Example program.
Screenshot:
Click the Any Configuration in the Omnet++ Ide to select the Configuration for the Example Program Simulation.
Screenshot:
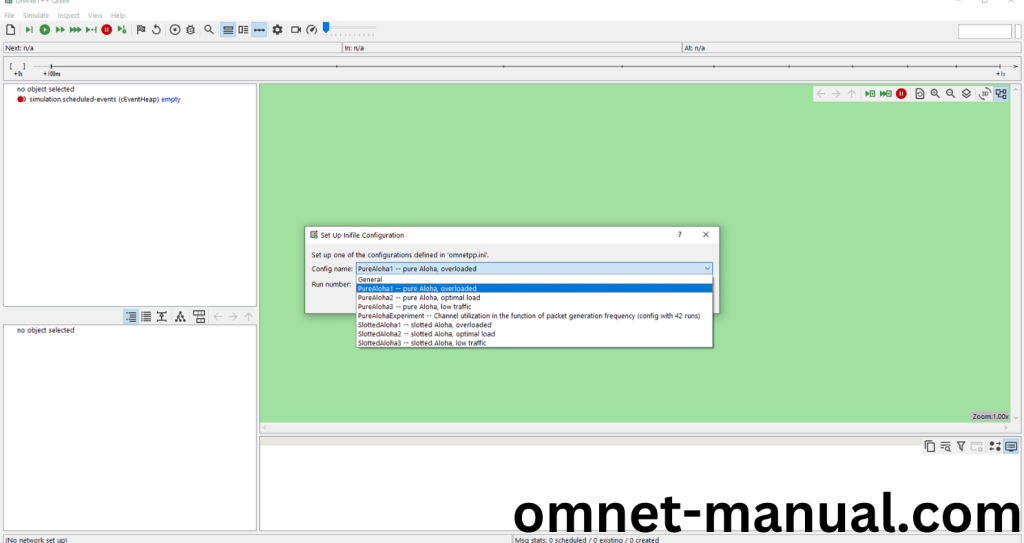
Click the Run Button in the Omnet++ Ide to simulate the Example Program.
Screenshot:
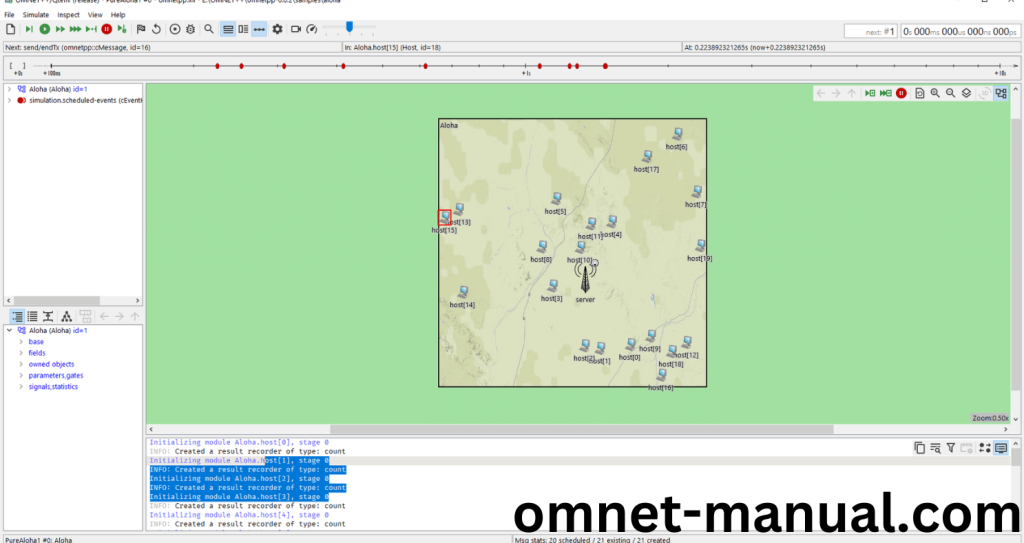
Screenshot:
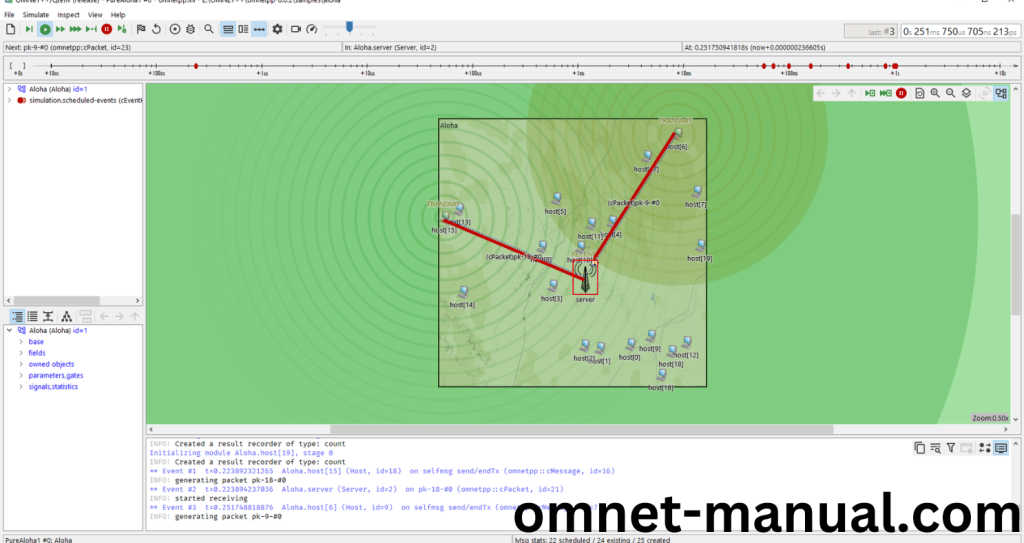
Screenshot:
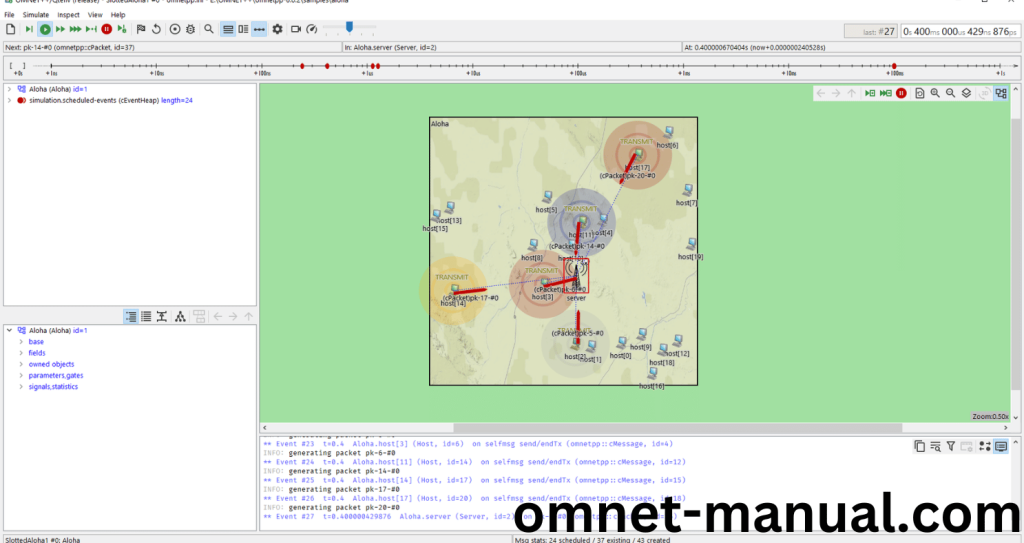
Next you need to locate to the Result folder there you will see the .sca file then you need to double click it.
Screenshot:
Next you need to click Finish to store the Statistics file recorded by this Header code.
Screenshot:
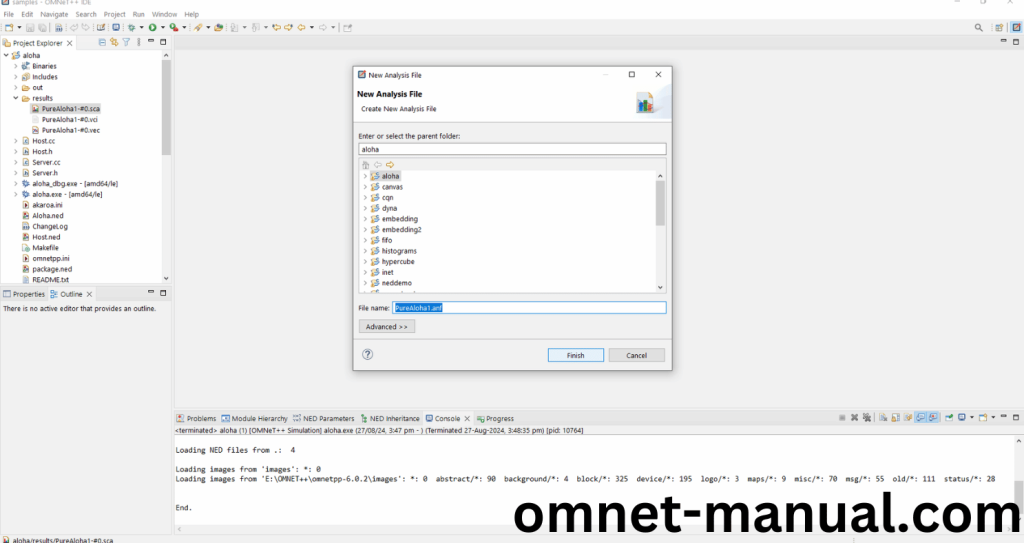
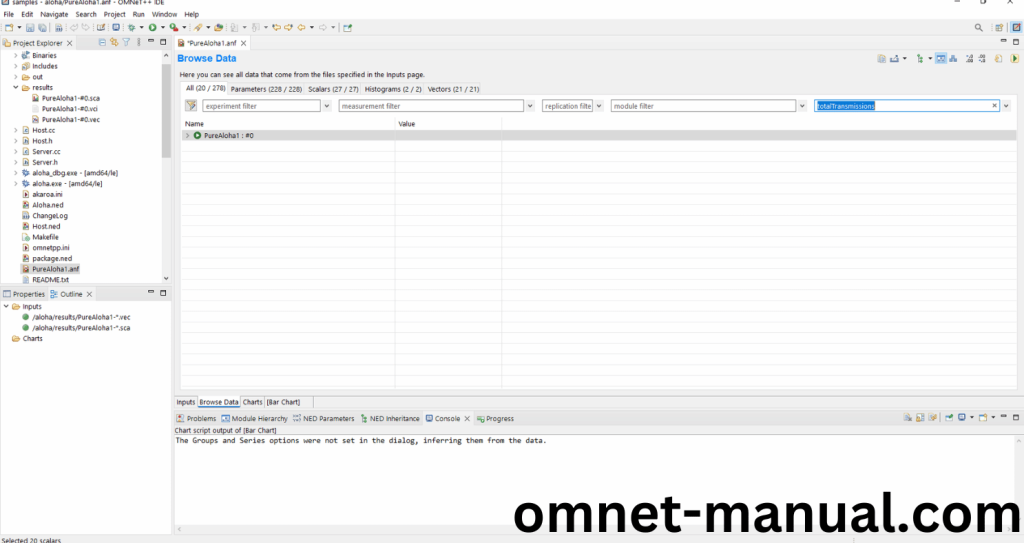
Next you need to click Browse Data and at last search bar , you need to search TotalTransmission that we had created in the code.
Screenshot:
Finally you can see the Recorded Result using cResultRecorder.h header file.
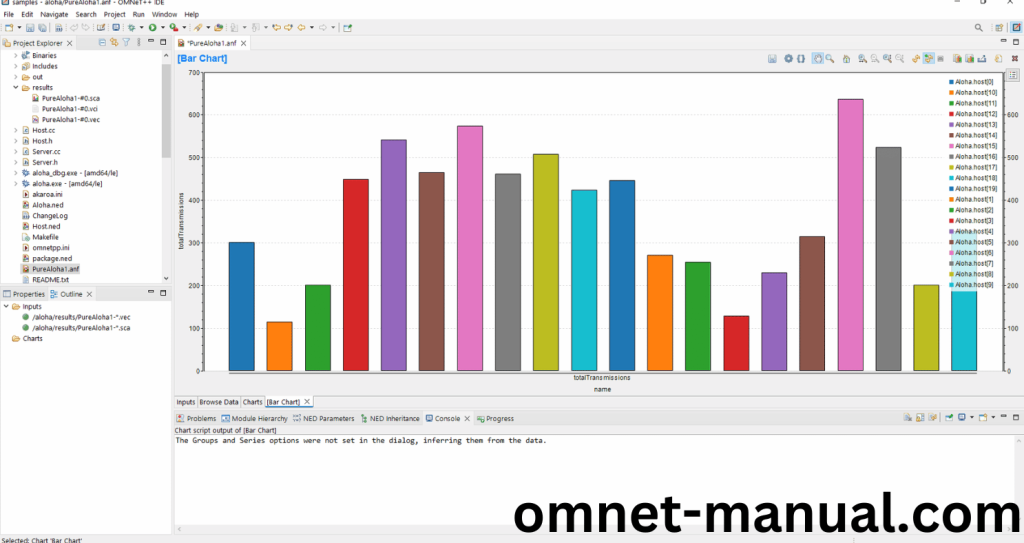
Simulation Completed Successfully by the Aloha Example Using cResultRecorder header.
To get best project execution ideas you van contact us for getting best outcomes, we will give you immediate reply.
